What Is Congestive Heart Failure? Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments Explained
Congestive heart failure is a condition in which your heart becomes insufficient to supply enough blood to the organs of your body. As a result, your heart fills with blood and becomes congested. Symptoms may vary from patient to patient, but usually they present with shortness of breath and edema (swelling in the legs and feet). Symptoms can be managed with medications, but you need a multidisciplinary approach for a permanent solution, which may include lifestyle changes, exercise, a balanced diet, and medications. Surgery can also be performed, like LVAD implantation, which may also need handling by using an LVAD shirt or LVAD gear. In many cases, congestive heart failure is diagnosed in the advanced stages, where the patient needs surgery or even a heart transplant for treatment.
In response to the congestive heart failure condition, your heart beats faster, puts greater force to supply the maximum amount of blood it can. When the heart is filled with blood, it builds up the fluid in the body and lungs, causing edema. With the minimum supply of blood, many organs do not function properly, including the kidneys, which may lead to kidney failure. For these reasons, congestive heart failure is a life-threatening disease that needs serious medical attention with emergent actions.
Heart failure is mostly common in older adults who have lived their whole lives with poor lifestyle habits. This means, if you are also living an unhealthy life with no proper diet and exercise, then you are at risk of developing congestive heart failure. Understand what congestive heart failure is, its risk factors, and how it affects the heart through this guide, and make some positive changes today to prevent future heart diseases.
What is congestive heart failure, and what causes CHF?
The function of the heart is to supply oxygen-rich blood to the whole body and organs to function properly. But when the heart does not supply enough blood due to congestion in the heart, it is termed as congestive heart failure. In congestive heart failure, the heart does not stop beating and supplying blood completely, but it does its job improperly. The heart becomes weak due to cardiomyopathy or other heart diseases, and works with more effort to supply blood. Ultimately, the fluid starts building up in the heart, lungs, and the lower extremities. Here are some of the other causes that can contribute to congestive heart failure.
- Coronary artery disease: The coronary artery is the main artery that supplies blood to the heart. When the coronary artery becomes affected, it disrupts the blood flow to the heart and lowers its capacity to pump blood.
- High blood pressure: When the pressure of the blood increases, it puts extra strain on the heart. By the time, the heart becomes weak, and can lead to congestive heart failure.
- Cardiomyopathy: What is cardiomyopathy? Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the muscles of the heart. Due to myopathies, the heart loses its ability to pump blood efficiently. It is one of the main causes of congestive heart failure.
- Heart valve disease: The valves of the heart make sure the blood flows smoothly in the right way. When these valves no longer perform their function, the heart works more than usual and becomes exhausted. As a result, heart functioning becomes compromised and can cause congestive heart failure.
- Congenital heart defects: These are diseases that are present at birth. Due to the condition, the heart becomes weak or stiff, and then the heart supplies insufficient blood, which can cause congestive heart failure.
- Arrhythmias: It is a term used to describe irregular heartbeats. When the heart beats too fast or too slow, it also affects the functioning, and hence can be the reason for developing congestive heart failure.
- Poor Lifestyle: Inactive lifestyle and poor diet lead to many heart diseases
- Viral infections affecting the heart cause inflammation, which can lead to insufficiency and diseases like congestive heart failure.
- Other factors: The diseases of other organs, like the kidneys and lungs, can also cause congestive heart failure.
What are the 4 stages of congestive heart failure?
The stages of heart failure describe the severity of the condition. Each stage has its own signs and symptoms and may require lifestyle modifications and medical attention. Here are the four stages described below:
Stage A: Stage A tells you that you are at risk of developing heart disease. In this stage, you may not have any symptoms or any type of structural deformity of the heart. You are also at risk if you have a positive family history of congestive heart failure, and you also have conditions like high blood pressure, obesity, or diabetes.
Stage B: It is a stage of pre-heart failure, where you may or may not have the symptoms of heart failure. In this stage, you may get a diagnosis of cardiomyopathy or valve disease.
Stage C: In this stage of congestive heart failure, you are diagnosed with the condition already, and you will have obvious structural damage to the heart. In this stage, you need medical attention otherwise, it can be a life-threatening disease.
Stage D: It is a stage of advanced heart failure where you will experience the symptoms of congestive heart failure even at rest, with no physical activity. In this stage, your doctor will recommend going for LVAD surgery or palliative care.
Congestive heart failure symptoms:
Congestive heart failure symptoms can be different for each patient, but generally, that are associated with this condition are listed below:
- Breathlessness or difficulty in breathing
- Chest pain
- Restlessness
- Reduced capacity for physical activity
- Swelling in legs, ankles, belly, and feet
- Irregular heartbeat
- Persistent cough
- Weight gain
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Difficulty focusing
- Increased frequency of urination, especially at nighttime
- Dizziness or fainting
- Bloating
Left-sided and Right-sided heart failure symptoms:
Left-sided heart failure occurs when the left ventricle fails to pump sufficient blood to the body. The right-sided heart failure occurs due to a right ventricular defect in supplying blood to the lungs. The heart failure symptoms due to left-sided heart failure can differ from the symptoms that occur due to right—sided heart failure. However, sometimes it can occur at the same time.
Left-Sided Heart Failure Symptoms:
- Fluid buildup due to congestion in the lungs
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing or wheezing
- Fatigue
- Difficulty in breathing when lying down
Right-Sided Heart Failure:
- Fluid buildup in the body and not the lungs
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and abdomen
- Enlarged liver or jugular veins
- Weight gain
- Nausea
- Bloating
Why are heart failure symptoms in women different than those in men?
Heart failure symptoms can also vary in men and women due to the hormonal and structural differences in the heart. Estrogen hormones that are present in women can affect the response of the body to heart strain and stress. Women with anxiety and depression may not experience the classic signs and symptoms of heart failure. Whereas men usually experience chest pain, shortness of breath. For this reason, it is more difficult to diagnose heart failure in women than in men because of their generalized symptoms like fatigue, sleep disturbances, and bloating.
Risk factors for congestive heart failure:
You may be at risk of developing congestive heart failure if you have any of the following conditions:
- Positive family history of congestive heart failure
- Hypertension
- History of a heart attack
- An imbalanced diet with high salt and sugar levels
- Sedentary lifestyle with almost no physical activity
- Disease of the coronary artery
- Heavy smoking and excessive alcohol intake
- If you are older than 65 years
- Chronic kidney disease can put strain on your heart
- Shortness of breath during sleep
Congestive heart failure treatment:
There is no hard and fast rule to treat a patient with congestive heart failure. Every patient has a unique set of symptoms and may need medical treatment according to those symptoms. Every patient needs individualized treatment, even if they are diagnosed with the same medical condition.
Treatment with Medications:
Some of the medications that are used in the congestive heart failure are described below:
- ACE (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme) inhibitors are medications that are used to relax blood vessels. These medicines are used to treat hypertension or high blood pressure and reduce the strain on the heart.
- Beta-blockers are another drug modification that reduces the heart rate and blood pressure. These drugs also reduce the workload of the heart.
- Diuretics are used to reduce fluid buildup caused by heart failure. These modifications reduce the edema of feet, abdomen, and lungs by removing excess fluid from the body.
- Aldosterone antagonist is also used in the treatment of congestive heart failure, which helps control blood pressure and fluid levels.
- Other medications that are used to treat patients with congestive heart failure may include ARNIs (, Digoxin, SGLT2 inhibitors (Sodium Glucose Transport 2 Inhibitor), and positive inotropes.
Treatment with lifestyle modification:
You may need to modify your lifestyle to prevent and manage the symptoms associated with congestive heart failure. Here are the positive lifestyle habits that you can follow:
- Include a low low-sodium diet in your meals, as that will help in reducing fluid retention.
- You may also need to limit your fluid intake to manage shortness of breath due to lung congestion.
- Include low to moderate physical activity according to your condition, as it helps to improve heart health.
- Lower your alcohol intake and quit smoking, as they damage the blood vessels and increase blood pressure.
- Managing your stress level may help manage overall health.
- You may also need to improve your sleep cycle to support mental health.
Treatment with surgical procedures:
Some of the surgical procedures that help support the functioning of the heart are as follows:
- An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a device that is implanted inside the heart to prevent sudden cardiac death.
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is a technique that helps to regulate heart rate and rhythm. It allows the lower part of the heart to pump in sync with the other.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a procedure that helps restore the blood supply of the heart and allows it to function properly. CABG is usually performed so that normal blood flow to the heart is impaired due to coronary artery disease.
- Conditions in which congestive heart failure occurs due to valve disease, heart valve repair, or replacement are performed.
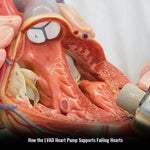
- When the left ventricle becomes unable to supply blood, a mechanical support device, known as a left ventricular assist device (LVAD), is implanted surgically. There are different LVAD types from which your doctor will choose the best option for you. You may need to buy clothing according to each type, like LVAD heartmate 3 clothing from our trusted brand, LVADGear.
- A heart transplant is an option for the patient whose heart cannot be repaired with medications or supportive surgical treatment. However, it may not be an appropriate treatment for every patient.
Palliative care and treatment:
When the patient has reached the stage where it cannot be treated surgically, or not even with a heart transplant. They need palliative treatment for symptom relief, like pain, breathlessness, and fatigue. For patients, emotional support is of significant importance, so proper counselling from professionals is a part of treatment.
How is congestive heart failure diagnosed?
Congestive heart failure diagnostic tests may involve the following:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
- Chest X-ray
- Blood tests
- Stress test
- Cardiac MRI
- CT scan
- Coronary angiography
- Cardiac catheterization
- Holter monitor
- Pulse oximetry
How long can you live with congestive heart failure?
Life expectancy after a 1st heart attack can vary from patient to patient and usually depends on the general health of the patient, the type of treatment used, and the response of each patient to particular treatment. Congestive heart failure life expectancy also depends on the stage and overall condition. Stage 3 heart failure life expectancy is several years with proper treatment, while stage 4 heart failure life expectancy is limited.
Conclusion:
Managing congestive heart failure requires an individualized approach that includes both lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. If you are dealing with a heart condition, you must have all the knowledge about the condition, including its causes, types, treatments, risks, and diagnostic tests to make an informed decision for yourself or a family member. For patients who have received surgical treatment like LVAD implantation, they usually live a life with improved quality by using a premium LVAD vest from our firm, LVADGear, that provides premium LVAD apparel and accessories. If you are at risk of developing congestive heart failure, you can still make positive changes in your lifestyle to improve or even reverse your heart health condition.
Prev post

LVAD Device Explained: Benefits, Risks, and Recovery
Updated on 28 April 2025
Next post

What is an LVAD? A Beginner's Guide for Patients & Families
Updated on 21 April 2025